Where Bed Bugs Hide In The Home?
The last thing anyone wants to think about are bed bugs hiding just out of plain sight, but it’s a reality. They don’t discriminate between clean/organized and dirty/messy environments, or public and personal spaces. However, cluttered environments with multiple hiding places can make bed bug control more difficult. Bed bugs can be attracted to many different warm-blooded vertebrate hosts (e.g., rodents, dogs, cats); however, humans are the preferred host.
Bed bugs live in a variety of environments associated with humans. These insects are attracted to warmth, moisture from your body, and CO2 and can detect these hosts seeking cues from approximately three feet away. Where bed bugs hide is related to blood meal host availability and blood feeding relies heavily on their ability to stay under cover until the opportunity arises. Let’s look at the most commonly asked questions about where bed bugs typically hide.
Where do Bed Bugs Hide During the Day?
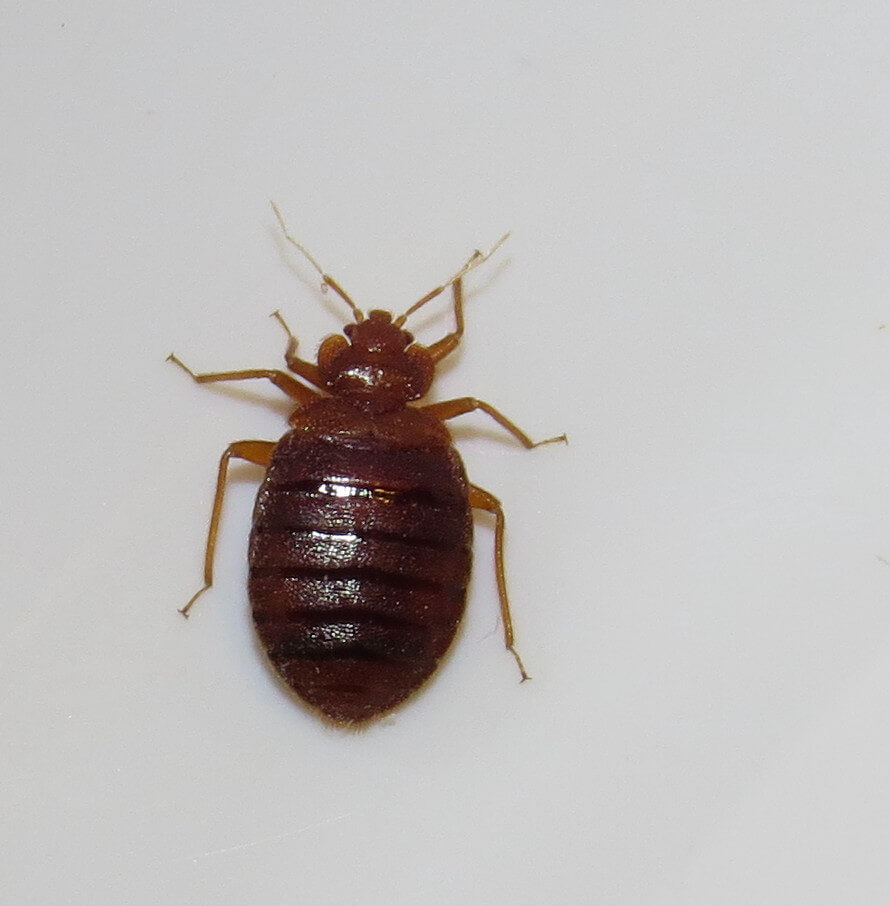

Bed bugs are nocturnal and mainly active at night, so what happens when the sun comes up? Bed bugs do not usually crawl for long distances and they don’t have wings so they tend to stay near potential blood meal hosts.
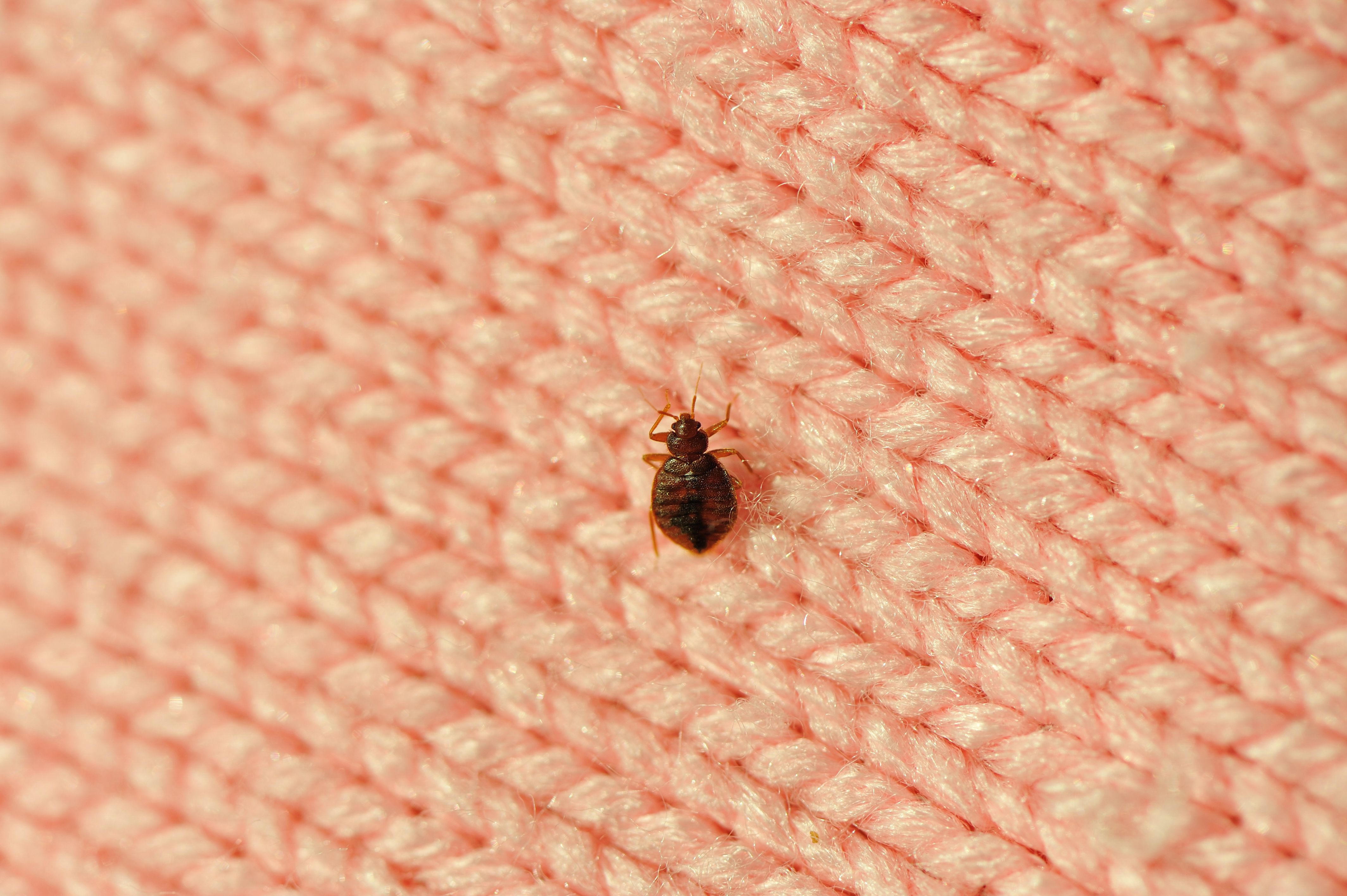
Evidence of where bed bug infestations may be found in a bed room include: bed frame, mattress and box spring. Bed bugs are only attached to hosts’ bodies during blood feeding. In between blood meals, bed bugs can also be found nearby on furniture, behind wallpaper and under the edge of carpet.
Their flattened shape makes it easy for the parasites to quickly hide in cracks and crevices, including walls, wood floors, electrical outlets and other narrow spots inside and outside your home or other area.
Can Bed Bugs Hide on Your Body?
Bed bugs gravitate towards people who remain inactive (e.g., sleeping) long enough to provide a blood meal, though you don’t need to worry about where bed bugs hide on your body for long term periods. Unlike ticks, bed bugs don’t attach themselves to a human host, but can be transported by humans in their belongings such as a coat, luggage or furniture.
Once established, bed bugs will instead travel from a hiding spot 5-20 feet away to blood feed. The blood feeding process usually lasts three to 10 minutes. While most people don’t know they’re being bitten during blood feeding, bites can result in itchy welts caused by a reaction to bed bug saliva and this can cause discomfort for up to a week or more
Once the blood feeding is complete, bed bugs retreat to their hiding spots to digest the blood. Male and female bed bugs require a blood meal between each of five nymphal stages. Once they reach adulthood, blood fed female bed bugs use the protein from the blood to develop eggs after mating. Under favorable conditions with access to blood meal hosts, the time between feedings usually ranges between five to 15 days and females can lay 10-50 eggs each batch. Bed bug adults are about the size of an apple seed.
Where do Bed Bugs Hide Their Eggs?
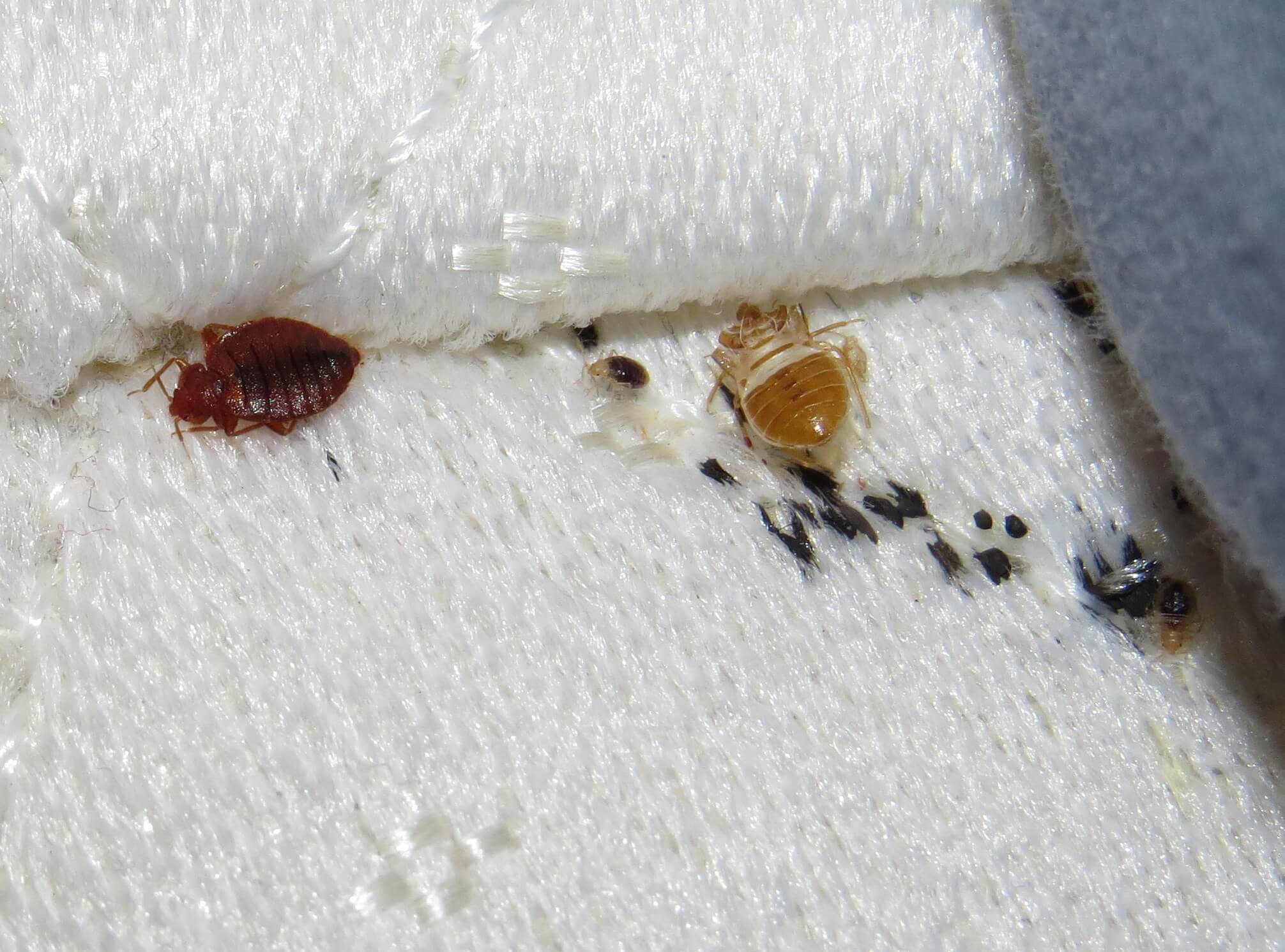
After mating, adult female bed bugs hide their eggs in secluded places. They’ll try getting as close to a food source as they can, and look for cracks and crevices, even seams of mattresses, mattress tags, and other hard to reach areas. A sticky substance produced by the female bed bug helps eggs stick to surfaces and each female can potentially produce hundreds of eggs during their lifetimes.
Bed bug eggs are tiny and white, about the width of a spaghetti noodle, and are difficult to observe closely without magnification. When temperatures are above 70°F, eggs can hatch in 7-10 days and this process takes longer at lower temperatures. Newly hatched nymphs (immature bed bugs) immediately go in search of a blood meal. Knowing where bed bugs hide their eggs can help investigators identify a potential issue and, help stop the issue from becoming an infestation








